

Project Momentum
Next Generation Knowledge Economy
Project Momentum
Next Generation Knowledge Economy
Chronicles of
BÖ§ZïK Inc.™ MSE/EPSE
Chronicles of
BÖ§ZïK Inc.™ MSE/EPSE


Project Momentum
Next Generation Knowledge Economy
Project Momentum
Next Generation Knowledge Economy
Chronicles of
BÖ§ZïK Inc.™ MSE/EPSE
Chronicles of
BÖ§ZïK Inc.™ MSE/EPSE
Newsflash! The Schedules for Physics II and
Pure Mathematics I & II are here!
ELECTRICAL QUANTITIES
1. Electric Charge, q
Physicists have arrived at the conclusion that electric charge is quantized. Its S.I. unit of measurement is the Coulomb, C.
The values of the charge associated with the elementary particles of an atom are:
These are relatively small values. As such, when computing the accumulation of charge, the general formula is used:
This summation is algebraic, meaning the sign of charges (positive or negative) must be considered when calculating the total.
2. The Mole Concept (revisited)
A standard quantity of the number of unit charge is called Avogadro’s Number, NA.
Numerically, 1 mole of electronic charge of any type is the quantity:
So, for n moles of N uniform charges q:
NB: the number of moles, n, is a ratio of the number of particles to Avogadro’s number. In general, it can also be computed using mass (m) and RAM or RMM for matter.
Current, Voltage, Work, Time
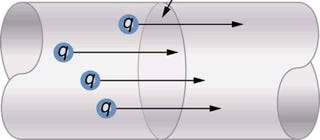
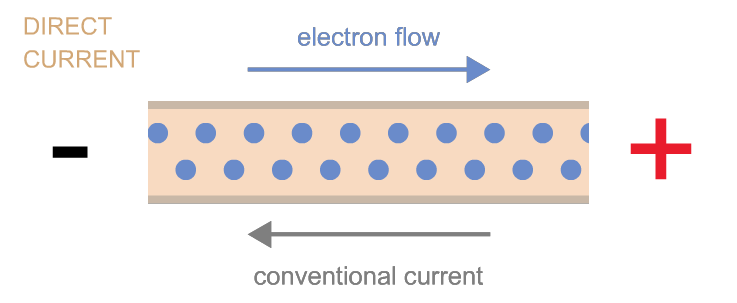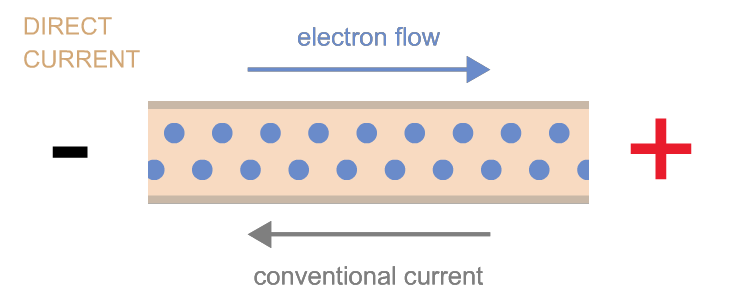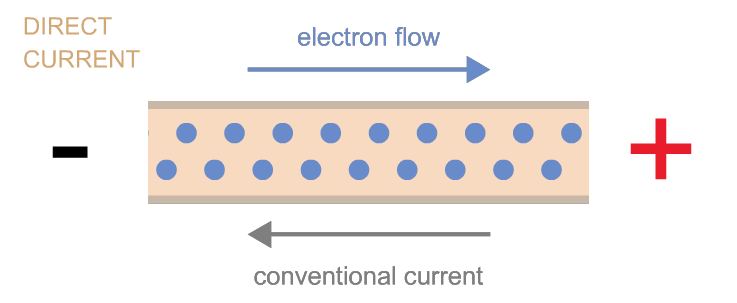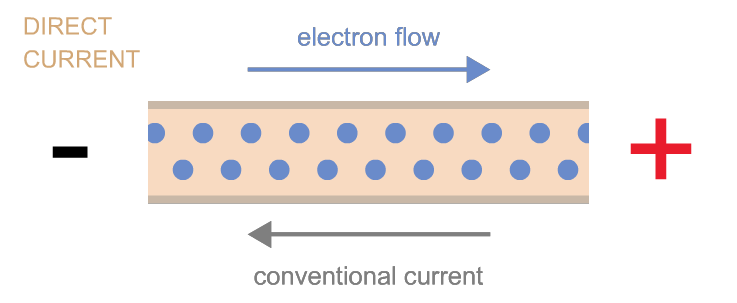
3. Electrical Current, I or I(t)
Electric Current is defined as the rate of flow of charges through a medium or pass a given point. Its S.I. unit of is the Ampere, A. Using this definition:
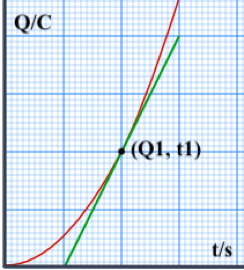
Both formulations are graphically represented as the slope (gradient) of the charge vs time graph!
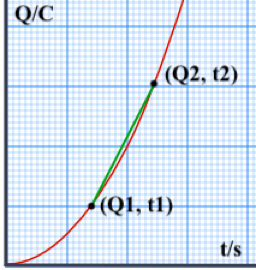
The instantaneous value is at a specific time while the average value is over a specific time interval. As such, the average current is also:
So, on the average, for a uniform current I, the total charge flowing in a given time is:
This product implies that the total charge is computed from the area under the current vs time graph!
4. Mobile Charges & Work Done
Charges can be moved by an electric field created by a potential difference (p.d.), ΔV (in the S.I. units of volts, V). Now, p.d. is defined as “work done per unit charge.” As such, on average:
Innovation by G. David Boswell
under the auspices of BÖ§ZïK Inc.™ EPSE & MSE Syndicates
Copyright 2020 | All Publication Rights Reserved: Now and Beyond.